ApplicationCommandLine
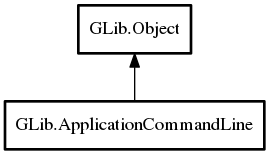
Object Hierarchy:
Description:
ApplicationCommandLine represents a command-line invocation of an application.
It is created by Application and emitted in the command_line signal and virtual function.
The class contains the list of arguments that the program was invoked with. It is also possible to query if the commandline invocation was local (ie: the current process is running in direct response to the invocation) or remote (ie: some other process forwarded the commandline to this process).
The GApplicationCommandLine object can provide the argc and argv parameters for use with the
OptionContext command-line parsing API, with the
get_arguments function. See gapplication-example-cmdline3.c
for an example.
The exit status of the originally-invoked process may be set and messages can be printed to stdout or stderr of that process. The lifecycle of the originally-invoked process is tied to the lifecycle of this object (ie: the process exits when the last reference is dropped).
The main use for ApplicationCommandLine (and the command_line signal) is 'Emacs server' like use cases: You can set the `EDITOR` environment variable to have e.g. git use your favourite editor to edit commit messages, and if you already have an instance of the editor running, the editing will happen in the running instance, instead of opening a new one. An important aspect of this use case is that the process that gets started by git does not return until the editing is done.
Normally, the commandline is completely handled in the command_line handler. The launching instance exits once the signal handler in the primary instance has returned, and the return value of the signal handler becomes the exit status of the launching instance.
static intThe complete example can be found here: gapplication-example-cmdline.c
command_line (GApplication *application,
GApplicationCommandLine *cmdline)
{
gchar **argv;
gint argc;
gint i;
argv = g_application_command_line_get_arguments (cmdline, &argc);
g_application_command_line_print (cmdline,
"This text is written back\n"
"to stdout of the caller\n");
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++)
g_print ("argument %d: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
g_strfreev (argv);
return 0;
}
In more complicated cases, the handling of the comandline can be split between the launcher and the primary instance.
static gbooleanIn this example of split commandline handling, options that start with `--local-` are handled locally, all other options are passed to the command_line handler which runs in the primary instance.
test_local_cmdline (GApplication *application,
gchar ***arguments,
gint *exit_status)
{
gint i, j;
gchar **argv;
argv = *arguments;
i = 1;
while (argv[i])
{
if (g_str_has_prefix (argv[i], "--local-"))
{
g_print ("handling argument %s locally\n", argv[i]);
g_free (argv[i]);
for (j = i; argv[j]; j++)
argv[j] = argv[j + 1];
}
else
{
g_print ("not handling argument %s locally\n", argv[i]);
i++;
}
}
*exit_status = 0;
return FALSE;
}
static void
test_application_class_init (TestApplicationClass *class)
{
G_APPLICATION_CLASS (class)->local_command_line = test_local_cmdline;
...
}
The complete example can be found here: gapplication-example-cmdline2.c
If handling the commandline requires a lot of work, it may be better to defer it.
static gbooleanIn this example the commandline is not completely handled before the command_line handler returns. Instead, we keep a reference to the ApplicationCommandLine object and handle it later (in this example, in an idle). Note that it is necessary to hold the application until you are done with the commandline.
my_cmdline_handler (gpointer data)
{
GApplicationCommandLine *cmdline = data;
// do the heavy lifting in an idle
g_application_command_line_set_exit_status (cmdline, 0);
g_object_unref (cmdline); // this releases the application
return G_SOURCE_REMOVE;
}
static int
command_line (GApplication *application,
GApplicationCommandLine *cmdline)
{
// keep the application running until we are done with this commandline
g_application_hold (application);
g_object_set_data_full (G_OBJECT (cmdline),
"application", application,
(GDestroyNotify)g_application_release);
g_object_ref (cmdline);
g_idle_add (my_cmdline_handler, cmdline);
return 0;
}
The complete example can be found here: gapplication-example-cmdline3.c
Namespace: GLib
Package: gio-2.0
Content:
Properties:
Creation methods:
Methods:
Inherited Members:
All known members inherited from class GLib.Object